Minimally Invasive Neurosurgery
What is Minimally Invasive Neurosurgery?
This global philosophy is based upon two fundamental aspects: to perform better operations and to achieve better results, in a safer way and with less blood loss for patients.
As well as other shared characteristics, all these techniques use minimal access surgery, including on occasion a microsurgical approach or via endoscopic routes, which allow for a quick post operative recovery.
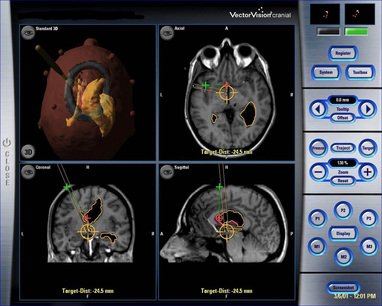
The majority of these techniques are based on improved visual control technology in surgery. From the lighting to microscopic surgery, including endoscopy, which nowadays has 3D intraoperative vision, as well as the virtual assistance that the neuronavigation systems offer, the neurosurgeon is able to inspect areas of the surgical field that were previously difficult to see. Of course, anatomic and aesthetic function preservation is always taken into consideration at the end of the surgery.
In the equally important post operative period, it is important to try and eliminate the patient’s pain and discomfort, in order to reduce to a minimum, wherever possible, the period spent in the ICU and in the post operation ward (neurosurgical ward). In any case, the experience of the neurosurgical team and common sense should dictate the priority of the surgery: the benefit to the patient.
- A global philosophy which aims to achieve more effective and efficient surgery.
- A surgical procedure which is safer and more comfortable for the patient.
- Surgical strategies which are less aggressive, better tolerated and which offer better results.
- The objective of modern Neurosurgery is neurological and psychological function preservation, therefore lowering the morbidity rate.
- It allows for a short preparation time prior to surgery.
- It allows for a more comfortable postoperative period compared to traditional techniques which in turn enables the patient to return to normal life more quickly.
- This philosophy can be applied to all neurosurgical procedures, be it brain or spine surgery.
This global philosophy is based upon two fundamental aspects: to perform better operations and to achieve better results, in a safer way and with less blood loss for patients.
As well as other shared characteristics, all these techniques use minimal access surgery, including on occasion a microsurgical approach or via endoscopic routes, which allow for a quick post operative recovery.
The majority of these techniques are based on improved visual control technology in surgery. From the lighting to microscopic surgery, including endoscopy, which nowadays has 3D intraoperative vision, as well as the virtual assistance that the neuronavigation systems offer, the neurosurgeon is able to inspect areas of the surgical field that were previously difficult to see. Of course, anatomic and aesthetic function preservation is always taken into consideration at the end of the surgery.
In the equally important post operative period, it is important to try and eliminate the patient’s pain and discomfort, in order to reduce to a minimum, wherever possible, the period spent in the ICU and in the post operation ward (neurosurgical ward). In any case, the experience of the neurosurgical team and common sense should dictate the priority of the surgery: the benefit to the patient.
Surgeons
|
Dr. Enrique Ferrer
Expertise: Brain Tumors Brain Surgery in Eloquent areas Endoscopic Skull Base Approach Epilepsy Surgery Parkinson's Disease Surgery Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Hydrocephalus Endoscopic Treatment |
Dr. Bartolomé Oliver
Expertise: Endoscopic Skull Base Approach Epilepsy Surgery Dynamic Stabilization of the Lumbar Spine Parkinson's Disease Surgery |